Campaigns have radically changed. As demonstrated in 2016, viral content and online message can have a powerful influence over the state of the race. Party platforms have less influence now than what is being discussed across the internet. The challenge for modern campaigns is to be able to effectively stay on top and get the message they want to reach voters.
With the midterm election fast approaching, it is essential for campaigns to know where they stand in the race. We know that there are many social media platforms out there and much of their content can be traced back to Reddit. With the speed at which viral content spreads, it is vital for campaigns to know their message is working or if your opponent’s attack ads are negatively affecting your campaign.
With the high stakes of today’s politic discourse, what can we learn by using machine learning to analyze how campaigns are being discussed? We will take the high profile campaign between Beto O’Rourke (D) and Ted Cruz (R) as our race to review in depth.
Applied Tools:
- webscraping
- APIs
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Data
Data was collected using the Reddit API to access posts from the subreddits for each campaign as well as the Texas subreddit. Since I planned on doing this multiple times and potentially for serveral different subreddits, I decided to write a function that was able to do so for any different subreddit title I decided to use.
#Generic function to scrap subreddit by name & how many times you want to repeat (next page of subreddit)
def reddit_scraper(subreddit, times):
url = "http://www.reddit.com/r/"+ subreddit +".json"
after = None #each query is limited to 25 post,
# 'after' grabs the last post and rewrites the url to grab the next 25 posts
for i in range(times):
posts = []
if after == None:
current_url = url
else:
current_url = url + '?after=' + after
print(current_url)
res = requests.get(current_url, headers={'User-agent': ''})
#print(res.status_code)
if res.status_code != 200:
print('Status error: ', res.status_code)
break
current_dict = res.json()
current_posts = [p['data'] for p in current_dict['data']['children']]
posts.extend(current_posts)
after = current_dict['data']['after']
time.sleep(4)
if i > 0:
current_df = pd.DataFrame(posts)
prev_posts = pd.read_csv(subreddit + '.csv')
all_posts = pd.concat([prev_posts,current_df])
all_posts.to_csv(subreddit + '.csv', index=False)
else:
current_df = pd.DataFrame(posts)
current_df.to_csv(subreddit + '.csv', index=False)
return all_posts.shape
To create the data to use for the project, I combined the post title with the post content to maximize the text content used in the model. This was necessary since many reddit posts related to both campaigns were just links to other pages and did not contain much discussion inside the post.
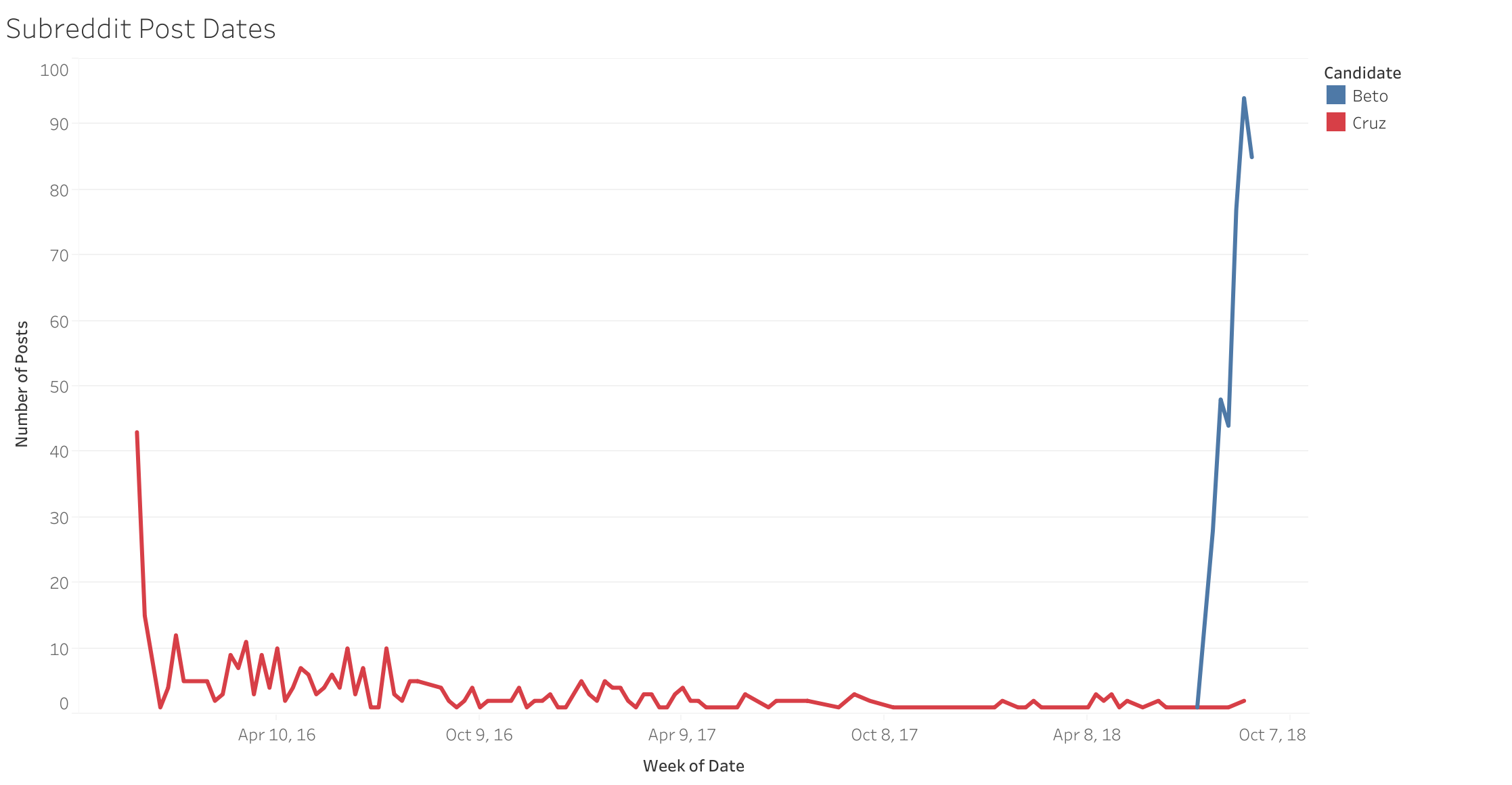
Additionally, it became very apparent how many more posts were occuring for the Beto campaign in the Reddit realm than the Cruz campaign. Since Reddit’s API is limited to the last 1000 posts, the timelines were very different depending on how active each campaign’s subreddit had been over time.
Each of the total posts per campaign were the same in the following chart, but show a very different timeline and frequency in posts over the last few months.
Models
After using TF-IDF to vectorize the text data, I applied multiple classifcation model types into a pipeline and optimized each with GridSearch on my training data to predict which subreddit the post came from. Exploring a variety of models initially helped give direction on which was able to perform relatively effectively and within the scope of the project.
Options in Pipeline
| Models | Vectorizer |
|---|---|
| - Logistic | - Count Vectorizer |
| - Random Forest | - TF-IDF Vectorizer |
| - Extra Trees | |
| - Gradient Boost | |
| - Multinomial Naive Bayes |
Ultimately, I ended up using Logistic Regression.
Once the model was finished, predictions were made on the test set and produced the following confusion matrix:
| Reddit Page | Predicted: Beto | Predicted: Cruz |
|---|---|---|
| Beto_for_Senate | 86 | 8 |
| TedCruz | 3 | 91 |
The model was able to successfully conduct binary classification with an accuracy score of 0.94. This seemed like good news but also too good to be true, so I explored what could be causing this high of an accuracy score.
During review of the coefficients, it was clear that the names of each candidate was the overwhelming influence on the model.
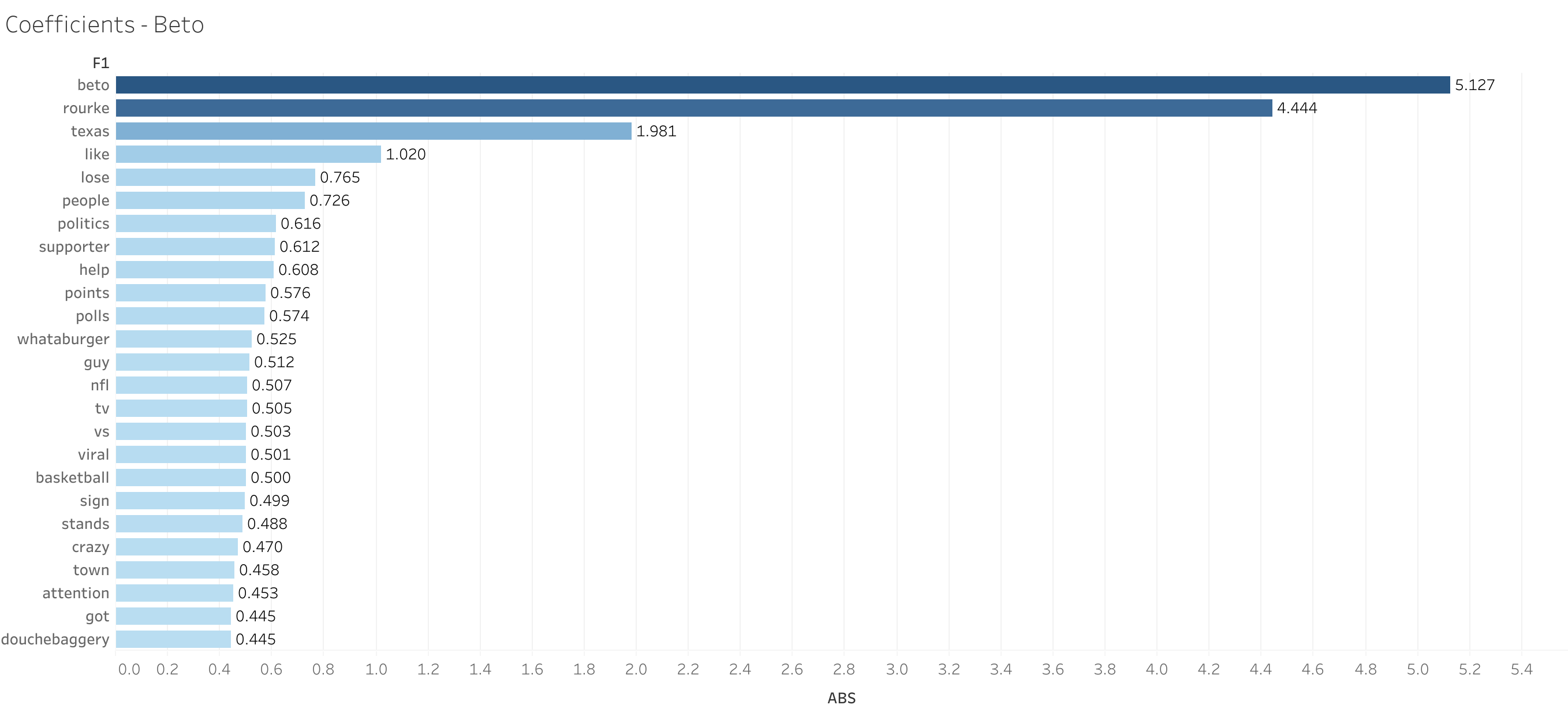
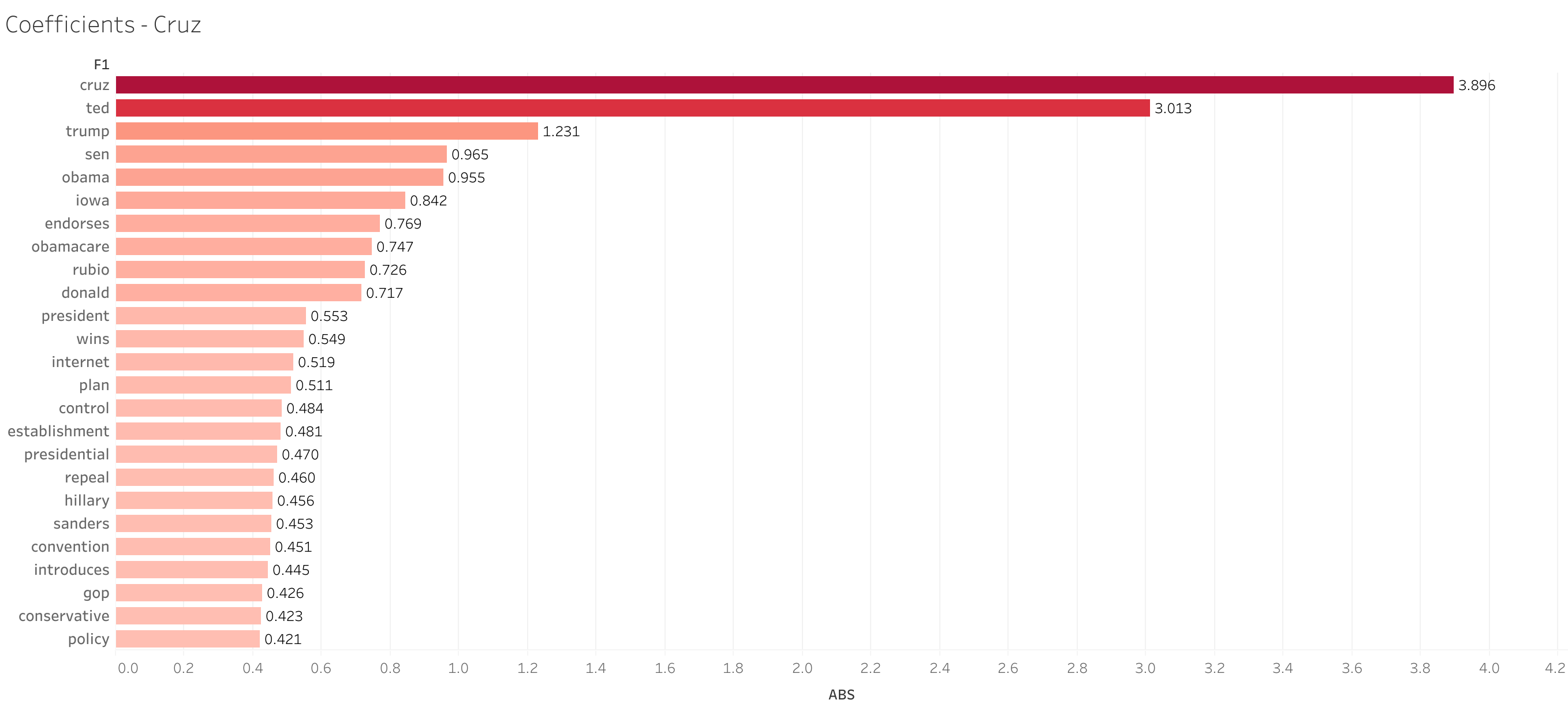
Changes to Model Accuracy
To further explore how each candidate name affected the accuracy of the overall model, I experimented with adding them to the list of stop words that the vectorizer ignored. I was able to produce almost the same accuracy by removing Ted Cruz from the corpus as I was able to do fine tuning the hyperparameters for models such as Support Vector Machines and GradientBoost.
1. Remove Candidates Names
0.729
2. Remove ‘Beto’ and ‘Rourke’
0.835
3. Remove ‘Ted’ and ‘Cruz’
0.910
The main reason for this to occur based on these findings was that posts from the Beto subreddit included more references to Ted Cruz and once removed, was able to seperate Beto posts just as effectively.
Addressing the Accuracy Paradox
What this ultimately comes down to is the model demonstrates the need to look at our results from a different perspective based on our data and how the accuracy paradox can come into play. The accuracy paradox states that a model wiht a given level of accuracy may have greater predictive power than models with higher accuracy. So while we are performing at a high accuracy, the best model may not be the one with highest accuracy since what allows us to generate a high score may not be what we really need in the end to find our true positive and negative predictions.
Collect more data: could help balance the dataset
Change you metric: Precision, Recall or F1 score
Oversample the data: Randomly sample the minority class to create more ‘fake’ data.
Penalized model: Bias the model towards the minority class.
Application
Predictions on Texas Subreddit
I wanted to understand the state of a third subreddit using what was trained to the model and if I could get the pulse of the Texas reddit. I used the same function I built earlier and isolated any post referencing a candidate or had a ‘politics’ flag.
Overall, a majority of post were predicted to be discussing topics indicating higher discussion relating to Beto over Cruz.
| The breakdown in post were: _Beto: _69% | Cruz: 31%__ |
Conclusion
Binary predictor can be effective in a first stage classification but can miss subtle things like sarcasm and word proximity. In the case of the subreddit posts from r/texas, posts with the highest probability as pro-Cruz were some of the strongest insults against him. Noticing and taking into account what your data actually contains is imperative to your ability to interpret the results.
Takeaways
Be careful for the Accuracy Paradox
Know your data source
Balance model complexity to your needs
To check out more about the project, visit the Github repo here.